Phase 2 - Gathering information
To adequately assess what is working well and what is causing challenges, it is crucial that you base the assessment (as far as possible) on existing, well-documented information. Therefore, you need to collect relevant documents and data that can be used to complete the worksheets associated with the assessment tools. These may include legislation, regulations, management plans and other planning documents, monitoring reports, impact assessment reports, disaster risk assessments, research projects and operational plans. For World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
properties, this needs to include the nomination file, the
Advisory Bodies
The three international organizations which are named in the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Convention to advise the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Committee in its deliberations are ICCROM (International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property), ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
The Advisory Bodies have the following functions:
Advise on the implementation of the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Convention in the field of their expertise
Provide expert advice on how to conserve and manage properties included on the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
List
Assist the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Centre in preparing the Committee’s documentation, the agendas of its meetings and in implementing the Committee’s decisions
Assist with the development and implementation of the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
List, the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Capacity Building Strategy, Periodic Reporting, and the strengthening of the effective use of the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Fund
Monitor the state of conservation of World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
properties (including through Reactive Monitoring missions at the request of the Committee and Advisory missions at the invitation of the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
)
Review requests for International Assistance
Attend meetings of the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Committee and the Bureau in an advisory capacity.
The Advisory Bodies are involved in the review of proposed actions and and any related impact assessments when they are requested by the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Committee.
’ evaluations, the World
Heritage
All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc.
Committee’s decisions, Periodic Reporting documents, State of Conservation reports and Reactive Monitoring mission reports, where applicable.
For heritage places with traditional management systems, customary practices and norms, the appropriate sources of information need careful consideration. Accessing, collecting and storing this information from a range of actors raises a number of issues (e.g. intellectual property rights) that need to be carefully addressed from the outset (see Phase I). The Facilitator’s Manual includes further guidance on this matter.
As you are collecting the information, you may realize that there are important gaps that cannot be addressed immediately and that can have implications for the level and scale of the assessment – particularly if this is the first time you are undertaking a management effectiveness assessment using the EoH 2.0 Toolkit. However, you should not feel discouraged or see information gaps as an obstacle to moving forward with the assessment. Instead, you should carefully consider how to tailor the assessment to take into account these constraints; the Facilitator’s Manual includes information to help you with this. At the same time, you can use the assessment as an opportunity to highlight information gaps and how they will be addressed in the future.
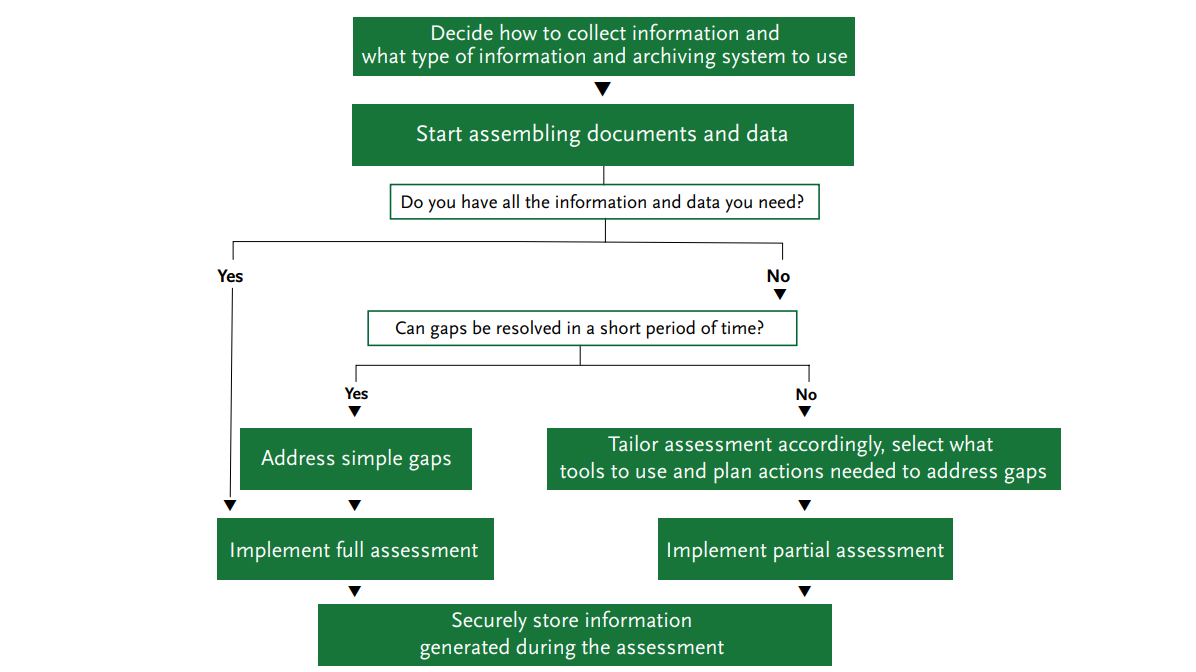
Figure 4.2: The process of collecting relevant information and data.



