Factors affecting the heritage place
-
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. are everything that can affect, directly or indirectly, positively or negatively, the state of conservation of a World Heritage property A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List. or other heritage place. - The same factor can affect different heritage places in different ways, depending on their heritage values and attributes, or it might have a different impact on different attributes of the same heritage place.
- Understanding the underlying cause of a factor helps managers identify why it is happening and ways of dealing with it.
- Some factors originate within the
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List. , while others are driven by actions or effects of actions undertaken beyond its boundaries. - A clear identification of how factors impact attributes is crucial to define appropriate management measures to tackle it.
- The identification of management measures requires an understanding of the cumulative effects of the different factors affecting the property, and of the severity and extent of the impacts on the attributes, in order to decide what the best response is and who will be responsible for implementing it.
Inscription of a property on the World Heritage All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc. List provides global recognition of its cultural and/or natural significance but is not in itself a guarantee that its attributes will be conserved and its OUV will be maintained. Many World Heritage All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc. properties are threatened, as the high number under the Reactive Monitoring process shows. Assessments such as IUCN’s World Heritage All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc. Outlook also show the increase of threats to natural properties, although, to some degree, all World Heritage All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc. properties are affected by a range of negative factors, normally called threats.
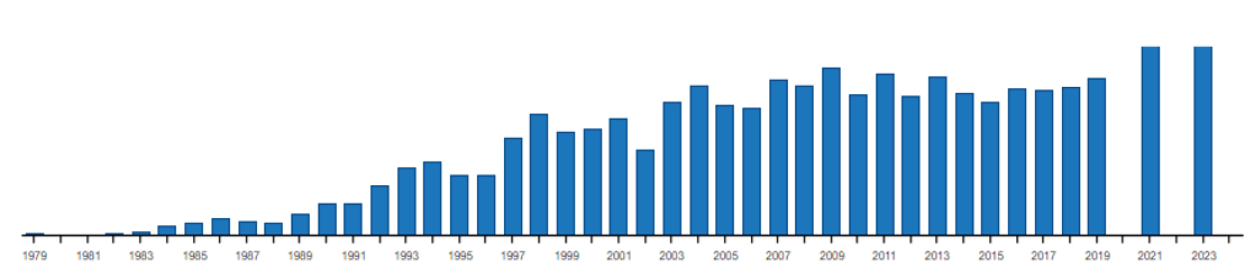
Figure 3.3 The number of properties examined each year on their state of conservation through the Reactive Monitoring process is continuously increasing. Source:
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
State of Conservation Information System.
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place.
can be defined as everything that can affect, directly and indirectly, positively and negatively, the state of conservation of a
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
or other heritage place. Some factors arise from natural processes and events, while others result from human activities, and most are a consequence of interrelated natural and human processes. Some factors originate within the
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
, while others are driven by actions or effects of actions undertaken beyond its boundaries. What may be a main factor in one heritage place may pose little concern in another and the same factor may have different impacts on different attributes within the same heritage place. For example, an invasive alien species may be a significant threat to ecosystem function or habitat viability but pose little threat to geological features. In recent years World Heritage properties are increasingly impacted by pressures of urban development that are rapid and inadequately controlled. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the range of factors affecting the heritage place is an important first step to inform management measures. To do this, information needs to be periodically collected and analysed to gather a detailed picture of what is really happening.
This includes understanding many aspects:
- What are the factors that are affecting the heritage place?
- Are these factors current or potential?
- What are the underlying causes that are the source of those factors?
- How are these factors impacting the attributes of the heritage place?
- What is the extent and severity of the impacts?
- What trends are associated with the factors – are they static, increasing or decreasing?
- What is the cumulative impact of the identified factors?
Impacts are the effects or consequences derived from or produced by a factor and how they affect the attributes and their state of conservation. Note that for there to be an impact, there must be a source of impact (e.g. vibrations from an industrial site), a receptor or attribute of the
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
that is affected (e.g. historic city) and a pathway or route by which the harmful action or material is able to reach the receptor (e.g. foundation rock beds). Impacts can be positive or negative as well as direct or indirect. As each heritage place is unique, so are the positive and negative factors that may affect its state of conservation at any given time.

Figure 3.4 The impact on a historic urban environment created by sound and vibration from a proposed action. An impact is the interaction of the factor with an attribute of the
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
. In this example, the vibration from the factor may have an impact on the buildings that constitute the attribute of a
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
and weaken their structural stability. Source: Guidance and Toolkit on
Impact
The effects or consequences of a factor on the attributes of the heritage place, both in terms of the attributes’ state of conservation and their ability to convey the heritage/ conservation values. An impact is the difference between a future environmental condition with the implementation of a development project, and the future condition without it. Note that for there to be an impact, there must a source of impact (e.g. noise from an industrial site), a receptor or attribute of the
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
that is affected (e.g. residents living nearby) and a pathway or route by which the harmful action or material is able to reach the receptor (e.g. the air). Impacts can be positive or negative, as well as direct or indirect, current or potential and originating within the heritage place, any existing buffer zone(s) and even beyond it.
See also: Direct impact,
Indirect impacts
Indirect impacts are impacts on the environment which are not a direct result of the project, often produced away from or as a result of a complex pathway. Sometimes referred to as ‘second’ or ‘third-level’ impacts, or ‘secondary’ impacts.
See also: Impact, Direct impacts, Cumulative impacts
, Cumulative impacts
Assessments in a World Heritage Context.
A list of factors was developed for World Heritage All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc. properties for use in Periodic Reporting, which allows the analysis of trends affecting World Heritage All inherited assets which people value for reasons beyond mere utility. Heritage is a broad concept and includes shared legacies from the natural environment, the creations of humans and the creations and interactions between humans and nature. It encompasses built, terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments, landscapes and seascapes, biodiversity, geodiversity, collections, cultural practices, knowledge, living experiences, etc. over time and across regions. This list of factors helps managers to systematically consider the factors which may be affecting a heritage place for management purposes and whether they are affecting it positively and negatively. This then provides an overview of the challenges and opportunities that the management system will need to respond to.
Having understood the social, economic, cultural and environmental context of a heritage place, it becomes easier to understand the underlying causes of the factors affecting the heritage place. This recognition helps managers to gain a more in-depth understanding of why a factor is happening, which can lead to identifying ways of addressing the causes rather than focusing on the symptoms of the impacts (see Tool 2 on p.36 of EOH Toolkit 2.0).
Thorough analysis of how a factor is currently affecting or could potentially affect a heritage place is needed to formulate adequate management measures. The standard list of factors used for the purposes of the Periodic Reporting exercise is intended to collect data across all World Heritage properties. To be used as a basis for identifying management measures at the property level, it needs to be applied to the specific situation on the ground and further detailed. For instance, one of the factors in the standard list is ‘ground transport infrastructure’ but in a detailed analysis of the factors affecting a specific heritage place, it is best to define the factor in a way that mentions the specific infrastructure, for example ‘construction of a new metro line’ or ‘road widening project through the north of the buffer zone.
When carrying out any such detailed analysis of the list of factors affecting a specific heritage place, it is important to remember the following points:
-
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. can affect the heritage place both positively and negatively. While negative impacts are often easier to identify, there may be a range of positive effects from factors. For example, upgraded transport infrastructure may overcome polluting traffic congestion, or new facilities help maintain the function of a historic port. Some factors can affect the heritage place both negatively and positively. For example, tourism may increase public support for conservation, but too many visitors can lead to overcrowded public spaces. In addition, some factors may be perceived negatively by some actors but positively by others. - The same factor can affect different heritage places in different ways, depending on their heritage values and attributes. Coastal erosion in a historic town can result in the degradation of archaeological structures that convey the town’s significance in a certain historic period. However, ongoing erosion at a geological site may be part of geological processes that have shaped the evolution of that heritage place over centuries and lead to new fossil exposures and discoveries. It is therefore necessary to understand the factor in relation to the specific heritage values and attributes of the heritage place.
- The same factor can have a different impact on different attributes of the same heritage place. For instance, it is unlikely that rising sea levels will impact all attributes of the heritage place at the same time or in the same way. Therefore, different management measures with different timeframes and levels of priority will be needed. Analysing the extent and severity of the impact of the factor on the different attributes will help in this regard. While the impacts of some factors can be relatively contained within an area of the heritage place (such as the construction of an underground carpark for visitors in a historic town centre impacting only a few buildings or the expansion of an existing hiking path in a mountain area), other factors can cause impacts on a much wider scale (such as the construction of a dam, air pollution, or lack of traditional materials to repair vernacular structures).
-
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. need to be considered not just for their current impact but also for how they may affect a heritage place in the future. Looking only at the current impact of a factor on a heritage place can be misleading. For example, an invasive species may only affect a small area of the heritage place at present; however, immediate action is needed to avoid it spreading out of control. Similarly, increasing numbers of visitors may not be a present concern; however, proactively engaging and influencing the local tourism policy can help avoid the arrival of unmanageable numbers of visitors during the peak season. While one new building in the buffer zone might be considered an acceptable change if it is part of a new construction trend, it will potentially have negative impacts on the heritage place over time. Therefore, it is best to analyse trends related to factors over time, including reasonable predictions for the near future (see 5.6). -
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. can cause impacts on a heritage place even when they originate outside. Some factors may have indirect impacts to a heritage place and it is necessary to be alert to that regardless of their physical distance from the place. Although the construction work of a new highway may not directly impact the attributes of a national park or an archaeological site, increased accessibility may allow increased numbers of visitors, poachers or illegal loggers access to the place, potentially having a negative effect on the vegetation or the archaeological remains. Therefore, any factor that could potentially affect the OUV of a World Heritage property A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List. must be considered.
Different factors will need different management measures: some may be addressed through routine maintenance works, others through specific conservation actions or management mechanisms. In circumstances where a transformative action is proposed or undertaken in or around the
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
– in particular when related to development projects and resource extraction – an impact assessment process is required. The cumulative and often interrelated effects of multiple factors must also be considered, particularly when coupled with risks due to disasters related to climate change and other natural and human induced hazards. In such cases, climate change vulnerability and disaster risk assessments need to be an integral part of the overall management planning processes for the heritage place.
Having identified a concrete list of the factors affecting a heritage place and analysed in detail the impacts they may have on the attributes of the heritage place, managers need to identify the best way to respond. For detailed analysis of the factors and what their potential impacts may be, more in-depth information and research conducted on a long-term basis may be needed.
Overall approaches to respond to different factors include:
-
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. related to management and institutional arrangements, such as a lack of adequate human resources or legal regulations, are better analysed through the use of management effectiveness assessment tools (see 6) which are able to identify where and what the gaps are. These factors could then be appropriately addressed through changes to the management system or in the subsequent cycle of management planning. -
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. that are actions or projects proposed for the future, such as the construction of large buildings or infrastructure, are better analysed through the use of impact assessment (see 5.8), which can help improve planning and decision-making processes so that World Heritage is considered. -
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. that are sudden ecological or geological events, or related to climate change effects, such as earthquakes, fires, floods or extreme weather events, are better addressed by developing disaster risk management (DRM) plans and climate action (see 5.7). -
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. that require consistent management actions over a certain period of time, such as loss of traditional agricultural practices or gentrification due to demographic changes, are best addressed within management planning processes (see 5.2 and 5.3). -
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. that require ongoing or frequent intervention, such as the control of invasive species or removal of weeds in archaeological structures, are best addressed through periodic maintenance works that should be included within the management plan (see 5.3).
Although various suggested management measures are given in this list, it should be remembered that the most effective approach to factors is a holistic one that links all these areas of management activity. This is because factors do not exist in isolation and can have complex interactions between them, causing cumulative effects or a chain reaction of negative or positive impacts. For example, risk preparedness for rising sea levels at a heritage place may include a project for flood defense systems, however, impact assessment could reveal that some elements of that project need adjustment to avoid negative impacts on attributes located on the seafront during construction of that defense system. Ongoing daily maintenance of a heritage place will also need to be linked to any response to factors so
that it supports the avoidance of more demanding and costly interventions at a later stage.
In each case of developing management measures to address factors, these points should be taken into consideration:
- A clear identification of which attributes are impacted is crucial.
Mapping the location, severity and extent of current and potential impacts in relation to specific attributes will help clarify the gravity of the current situation and predict future trends. Such analysis will indicate which factors need to be addressed urgently (or in which sequence) and help establish management priorities. For example, freshwater wetlands within a natural
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
may be more sensitive to changing temperatures due to climate change than
other areas within the property. Certain buildings within an historic town suffering from neglect over decades may be at a higher risk of collapsing than others. In these cases it will be necessary to map which attributes are the most impacted to identify management priorities: which wetlands or waterlogged sites are most affected within which timeframes and therefore require more immediate management interventions. This type of analysis will also help establish priorities
between different management measures to respond to different factors. For instance, tackling the potential collapse of buildings in an advanced stage of decay would need to be addressed more immediately over measures to improve heritage interpretation that would require a longer-term response.
- Understanding the state of conservation of attributes over time is important.
Information on factors affecting a
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
at the time of its inscription can provide a useful baseline for assessing the current state of conservation of the property and understanding whether the situation is improving or not. By comparing the current situation with past data, changes that have taken place since inscription can be identified, and a check made on whether new factors have arisen and recurrent ones are being dealt with effectively. The Periodic Reporting exercise can also provide complementary updates on factors (see 5.6).
- Effective monitoring of the factors affecting the heritage place will also help detect challenges at an early stage.
Monitoring should pinpoint the need for early and more achievable management measures. Sometimes further research or studies may be needed before a response is fully defined and implemented. For instance, the stability of a structure may need to be studied in regard to changing weather patterns and the amount of exposure it has, to devise suitable intervention methods. The detection and control of an invasive species would need careful study and research to determine the best method of reducing the impact on the attributes but also preventing the spread of the species itself.
- It is better to take proactive measures to avoid negative impacts, rather than react to a problem after it has arisen.
For example, an old electricity system in a wooden building may need to be proactively replaced to avoid a fire. The potential construction of high-rise buildings in the vicinity of an urban settlement or the issue of a logging license around a forest, may require a revision to the urban planning strategy or land-use plan from a heritage perspective, which will be useful for scoping out unacceptable types of development in a proactive way.
- The identification of management measures also requires identifying who will be responsible for implementing those measures and ensuring adequate resources are available.
Many measures to address factors are not within the mandate of heritage managers and/or need the concerted action of multiple actors. In these cases, heritage managers need to establish working relationships with those actors so that they are aware of the World Heritage implications and cooperation can be established. For example, a cultural landscape would benefit from the land management department of the municipality coordinating with heritage managers to make sure that land-use regulations in the buffer zone avoid encroaching development.

Figure 3.5 This list is used to understand the range of factors that can potentially affect World Heritage properties. For full list, visit the World Heritage website. Source: UNESCO
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
.
Within the World Heritage system, State of Conservation (SOC) reports may refer to two different documents, one of which is by
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
(commonly called the State Party SOC report) and the other by the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
and
Advisory Bodies
The three international organizations which are named in the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
to advise the World Heritage Committee in its deliberations are ICCROM (International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property), ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
The Advisory Bodies have the following functions:
Advise on the implementation of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
in the field of their expertise
Provide expert advice on how to conserve and manage properties included on the World Heritage List
Assist the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
in preparing the Committee’s documentation, the agendas of its meetings and in implementing the Committee’s decisions
Assist with the development and implementation of the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World Heritage List, the World Heritage Capacity Building Strategy, Periodic Reporting, and the strengthening of the effective use of the World Heritage Fund
Monitor the state of conservation of World Heritage properties (including through Reactive Monitoring missions at the request of the Committee and Advisory missions at the invitation of the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
)
Review requests for International Assistance
Attend meetings of the World Heritage Committee and the Bureau in an advisory capacity.
The Advisory Bodies are involved in the review of proposed actions and and any related impact assessments when they are requested by the World Heritage Committee.
in the Reactive Monitoring process.
The
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
and
Advisory Bodies
The three international organizations which are named in the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
to advise the World Heritage Committee in its deliberations are ICCROM (International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property), ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
The Advisory Bodies have the following functions:
Advise on the implementation of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
in the field of their expertise
Provide expert advice on how to conserve and manage properties included on the World Heritage List
Assist the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
in preparing the Committee’s documentation, the agendas of its meetings and in implementing the Committee’s decisions
Assist with the development and implementation of the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World Heritage List, the World Heritage Capacity Building Strategy, Periodic Reporting, and the strengthening of the effective use of the World Heritage Fund
Monitor the state of conservation of World Heritage properties (including through Reactive Monitoring missions at the request of the Committee and Advisory missions at the invitation of the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
)
Review requests for International Assistance
Attend meetings of the World Heritage Committee and the Bureau in an advisory capacity.
The Advisory Bodies are involved in the review of proposed actions and and any related impact assessments when they are requested by the World Heritage Committee.
prepare SOC reports to inform the World Heritage Committee on the conditions of specific properties which are under threat and for which the Reactive Monitoring process has been or is to be activated. These reports are based on information and studies prepared by the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
submitted as the State Party SOC report, whenever ‘exceptional circumstances occur or work is undertaken which may have an impact on the OUV of the property or its state of conservation’ (Operational Guidelines, paragraph 169).
The SOC reports prepared by the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
jointly with the
Advisory Bodies
The three international organizations which are named in the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
to advise the World Heritage Committee in its deliberations are ICCROM (International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property), ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
The Advisory Bodies have the following functions:
Advise on the implementation of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
in the field of their expertise
Provide expert advice on how to conserve and manage properties included on the World Heritage List
Assist the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
in preparing the Committee’s documentation, the agendas of its meetings and in implementing the Committee’s decisions
Assist with the development and implementation of the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World Heritage List, the World Heritage Capacity Building Strategy, Periodic Reporting, and the strengthening of the effective use of the World Heritage Fund
Monitor the state of conservation of World Heritage properties (including through Reactive Monitoring missions at the request of the Committee and Advisory missions at the invitation of the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
)
Review requests for International Assistance
Attend meetings of the World Heritage Committee and the Bureau in an advisory capacity.
The Advisory Bodies are involved in the review of proposed actions and and any related impact assessments when they are requested by the World Heritage Committee.
contain a summary of the issues emerged relating to conservation, protection and management, factors affecting the property and a draft decision with recommendations for action. The reports and the draft decisions are reviewed by the World Heritage Committee at the subsequent session (meeting), and, if necessary, discussed, and eventually adopted. The World Heritage Committee decisions concerning the state of conservation of World Heritage properties require
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
to report within a specific timeframe on actions taken to implement the recommendations included in the decisions. When there is a common issue that affects more than one
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
, it may be adopted through an omnibus decision.
Not all SOC reports and draft decisions are open for discussion during the World Heritage Committee session. Many are adopted as they stand without being discussed by the World Heritage Committee. Where a property is proposed for inclusion in the List of World Heritage in Danger or for delisting from either the Danger List or the World Heritage List, the SOC report is always discussed by the World Heritage Committee.
In addition to these processes,
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
are encouraged to provide information on their intention to undertake or authorize in an area protected under the Convention major restorations or new constructions which may affect the OUV of the property, under paragraph 172 of the Operational Guidelines. If information on emerging threats to the OUV, integrity and authenticity of a
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
are received by the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
from third parties, the World Heritage
Centre takes steps to verify the reports and then requests information from the State Party on their nature and seriousness. The State Party is then invited to provide information in response. In many of these cases, the information provided through the different sources is reviewed by the
Advisory Bodies
The three international organizations which are named in the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
to advise the World Heritage Committee in its deliberations are ICCROM (International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property), ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
The Advisory Bodies have the following functions:
Advise on the implementation of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
in the field of their expertise
Provide expert advice on how to conserve and manage properties included on the World Heritage List
Assist the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
in preparing the Committee’s documentation, the agendas of its meetings and in implementing the Committee’s decisions
Assist with the development and implementation of the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World Heritage List, the World Heritage Capacity Building Strategy, Periodic Reporting, and the strengthening of the effective use of the World Heritage Fund
Monitor the state of conservation of World Heritage properties (including through Reactive Monitoring missions at the request of the Committee and Advisory missions at the invitation of the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
)
Review requests for International Assistance
Attend meetings of the World Heritage Committee and the Bureau in an advisory capacity.
The Advisory Bodies are involved in the review of proposed actions and and any related impact assessments when they are requested by the World Heritage Committee.
, which provide technical reviews and related recommendations to the State Party to remove or reduce potential negative impacts from the property.
In the case where information received confirms that there are threats to the property based on a joint assessment by the
Advisory Bodies
The three international organizations which are named in the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
to advise the World Heritage Committee in its deliberations are ICCROM (International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property), ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
The Advisory Bodies have the following functions:
Advise on the implementation of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
in the field of their expertise
Provide expert advice on how to conserve and manage properties included on the World Heritage List
Assist the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
in preparing the Committee’s documentation, the agendas of its meetings and in implementing the Committee’s decisions
Assist with the development and implementation of the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World Heritage List, the World Heritage Capacity Building Strategy, Periodic Reporting, and the strengthening of the effective use of the World Heritage Fund
Monitor the state of conservation of World Heritage properties (including through Reactive Monitoring missions at the request of the Committee and Advisory missions at the invitation of the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
)
Review requests for International Assistance
Attend meetings of the World Heritage Committee and the Bureau in an advisory capacity.
The Advisory Bodies are involved in the review of proposed actions and and any related impact assessments when they are requested by the World Heritage Committee.
and the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
, the case is presented to the World Heritage Committee at its next session: the property then enters the formal Reactive Monitoring process.
After the World Heritage Committee meeting, the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
forwards the Committee’s decisions to
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
within a month of the meeting (paragraph 168) to ensure prompt action to redress threats.
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
, usually through their national focal points, are responsible for forwarding this information to the managers of the properties concerned.
The SOC reports and World Heritage Committee’s decisions are accessible at the website of the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
, allowing managers to consult all past decisions adopted at its sessions throughout the years, along with a range of other information about each
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
.
Adapted from: Operational Guidelines (2024), Managing Cultural World Heritage (2012), Managing Natural World Heritage (2011).
The List of World Heritage in Danger is conceived as a mechanism for international cooperation within the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
. Its purpose is to raise international attention about the threats faced by a
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List.
, to mobilize technical assistance and to secure the resources needed to carry out operations to mitigate or remove these threats. The concerned State Party can request International Assistance within the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
to mobilize resources at local, national and international levels to undertake such operations.
The criteria for the inscription of a property on the List of World Heritage in Danger are set out in the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
and further defined in the Operational Guidelines to determine whether the property is facing ascertained and/or potential danger. Meeting one of these criteria suffices for the World Heritage Committee to inscribe the property on this List.
When a property is inscribed on the List of World Heritage in Danger, the Committee requests
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
to implement a set of actions called Corrective Measures to remove the property’s threats and restore any deteriorated attributes within a specific timeframe.
The ‘Desired State of Conservation for the Removal of the property from the List of World Heritage in Danger’ – often abbreviated as DSOCR or desired state of conservation – is a defined state of conservation that a property must reach to demonstrate that it is no longer threatened by serious and specific danger, and to enable its removal from the List of World Heritage in Danger. It is achieved through the successful implementation of the Corrective Measures.
The DSOCR should be drafted by the State Party, in collaboration with the managers and other relevant actors. It is submitted to the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
along with the annual report on the State of Conservation of the property for review and adoption. Exchanges with the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
and the
Advisory Bodies
The three international organizations which are named in the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
to advise the World Heritage Committee in its deliberations are ICCROM (International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property), ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
The Advisory Bodies have the following functions:
Advise on the implementation of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
in the field of their expertise
Provide expert advice on how to conserve and manage properties included on the World Heritage List
Assist the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
in preparing the Committee’s documentation, the agendas of its meetings and in implementing the Committee’s decisions
Assist with the development and implementation of the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World Heritage List, the World Heritage Capacity Building Strategy, Periodic Reporting, and the strengthening of the effective use of the World Heritage Fund
Monitor the state of conservation of World Heritage properties (including through Reactive Monitoring missions at the request of the Committee and Advisory missions at the invitation of the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
)
Review requests for International Assistance
Attend meetings of the World Heritage Committee and the Bureau in an advisory capacity.
The Advisory Bodies are involved in the review of proposed actions and and any related impact assessments when they are requested by the World Heritage Committee.
and joint Reactive Monitoring missions are deployed to understand the challenges and to support
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
and managers in seeking solutions to the threats, as well as in preparing and finalizing the DSOCR. Once adopted, the DSOCR and corrective measures serve as the indicators to determine if the property can be removed from the Danger List or not.
It is fundamental that the State Party is fully engaged, from the managers to all relevant actors at local and national levels, in developing the DSOCR and the corrective measures. The involvement of all relevant actors ensures that these measures are feasible and can be implemented and the desired state of conservation is shared and agreed upon thus facilitating its achievement. For these processes, the State Party can request technical/advisory missions as well as International Assistance; the Committee will also extend its cooperation in negotiations to obtain assistance from other donors where necessary.
From a management perspective, the inscription on the List of World Heritage in Danger, with its set of corrective measures to be implemented and a DSOCR to be reached within a specific timeframe, generally demands that the management plan is revisited and modified: different priorities, further actions and resources are often needed to address the concerns of the World Heritage Committee. These changes may affect one or more management cycles, depending on the scope of the corrective measures and the timeframe necessary for their implementation. The implementation of corrective measures to achieve the DSCOR may demand changes in the governance and management arrangements for the property, updates in legislation or the halting of certain projects.
Progress made in implementing the corrective measures and in approaching the DSOCR, together with any information provided by the State Party, will be included in annual SOC reports submitted to the World Heritage Committee.
Based on the regular review of the State of Conservation, the World Heritage Committee shall decide, in consultation with the State Party concerned and with the assistance of the
Advisory Bodies
The three international organizations which are named in the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
to advise the World Heritage Committee in its deliberations are ICCROM (International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property), ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
The Advisory Bodies have the following functions:
Advise on the implementation of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
in the field of their expertise
Provide expert advice on how to conserve and manage properties included on the World Heritage List
Assist the
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
, is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention.
in preparing the Committee’s documentation, the agendas of its meetings and in implementing the Committee’s decisions
Assist with the development and implementation of the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World Heritage List, the World Heritage Capacity Building Strategy, Periodic Reporting, and the strengthening of the effective use of the World Heritage Fund
Monitor the state of conservation of World Heritage properties (including through Reactive Monitoring missions at the request of the Committee and Advisory missions at the invitation of the
States Parties
The countries which have adhered to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind.
) (UNESCO, 1972).
)
Review requests for International Assistance
Attend meetings of the World Heritage Committee and the Bureau in an advisory capacity.
The Advisory Bodies are involved in the review of proposed actions and and any related impact assessments when they are requested by the World Heritage Committee.
whether:
- additional measures are required to conserve the property;
- the property can be removed from the List of World Heritage in Danger, if the main threats have been addressed;
- to delete the property from the World Heritage List it is considered that the property has deteriorated to the extent that it has lost those characteristics which determined its inscription from the outset.
The procedure for the deletion of a property from the World Heritage List is set out in paragraphs 192 – 198 of the Operational Guidelines.
Adapted from: Operational Guidelines (2024), Managing Cultural World Heritage Properties (2011).
- Have the factors affecting the
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List. or other heritage place been identified and documented in information sources that are used regularly (e.g. management plan)? - Is there a detailed understanding of the factors affecting the property and their underlying causes and impacts? Or is available knowledge mainly limited to a list of factors?
- Are the factors readily available for consultation by all actors engaged with the management of the heritage place?
- Have positive factors been identified? Or is the list limited to negative factors or threats?
- Have factors originating from outside the property been identified, e.g. within the buffer zone(s), or the wider setting?
- In some cases, one factor (e.g. changing in precipitation patterns) can impact more than one attribute (e.g. a wetland and an agricultural practice), and in different ways. Are these diverse relationships well understood?
- Have the relationships between factors and the potential cumulative and multiplying effects of different impacts been considered?
- A list of factors affecting the properties,
World Heritage Centre
The UNESCO World Heritage Centre is a technical administrative body within UNESCO, established in 1992 and appointed by the Director-General of UNESCO. It acts as the Secretariat of the
World Heritage Convention
The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage is an international treaty adopted by the UN in 1972 that defines the kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List for their Outstanding Universal Value for all humankind. Commonly known as the World Heritage Convention, it establishes how the international community as a whole is responsible for
the protection of such heritage and sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites that may be eligible for inscription onto the World Heritage List and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the sites situated on its territory that have been recognized as being of Outstanding Universal Value, but also to protect its national heritage and to be involved in international efforts to protect, conserve and promote the heritage of humankind. , is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage, and ensures the day-to-day management of the Convention. , Paris, UNESCO. - UNESCO, ICCROM, ICOMOS, IUCN (2023). Tool 2.
Factors
Everything that can affect, positively and negatively, the values and attributes of the heritage place and its state of conservation. Negative factors are usually called threats.
How factors affect a property needs to be analysed through a series of parameters namely the underlying causes that are the source of the factor, their origin (if originating within or outside the property), the current and potential impacts deriving from the factor and the extent and severity of the impacts on the attributes of the heritage place. affecting the property. In Enhancing Our Heritage Toolkit 2.0, pp. 36-39, Paris, UNESCO. - UNESCO, ICCROM, ICOMOS, IUCN (2022). Guidance and Toolkit for
Impact
The effects or consequences of a factor on the attributes of the heritage place, both in terms of the attributes’ state of conservation and their ability to convey the heritage/ conservation values. An impact is the difference between a future environmental condition with the implementation of a development project, and the future condition without it. Note that for there to be an impact, there must a source of impact (e.g. noise from an industrial site), a receptor or attribute of the
World Heritage property
A cultural, natural or mixed heritage place inscribed on the World Heritage List and therefore considered to be of OUV for humanity. The responsibility for nominating a property to the World Heritage List falls upon the State(s) Party(ies) where it is located. The World Heritage Committee decides whether a property should be inscribed on the World Heritage List, taking into account the technical recommendations of the Advisory Bodies following rigorous evaluation processes.
When used as a general term, World Heritage refers to all the natural, cultural and mixed properties inscribed on the World Heritage List. that is affected (e.g. residents living nearby) and a pathway or route by which the harmful action or material is able to reach the receptor (e.g. the air). Impacts can be positive or negative, as well as direct or indirect, current or potential and originating within the heritage place, any existing buffer zone(s) and even beyond it.
See also: Direct impact, Indirect impacts Indirect impacts are impacts on the environment which are not a direct result of the project, often produced away from or as a result of a complex pathway. Sometimes referred to as ‘second’ or ‘third-level’ impacts, or ‘secondary’ impacts.
See also: Impact, Direct impacts, Cumulative impacts , Cumulative impacts Assessments in a World Heritage Context. - UNESCO, ICCROM, ICOMOS, IUCN (forthcoming). Managing Disaster Risks and Building Resilience for World Heritage. For disaster risk factors: Managing Disaster Risk for World Heritage.
- UNESCO (2023). Glossary within the Policy Document on Climate Action A policy, plan, programme or project. for World Heritage.
- UNESCO Urban Heritage Atlas.
- IUCN World Heritage Outlook.



